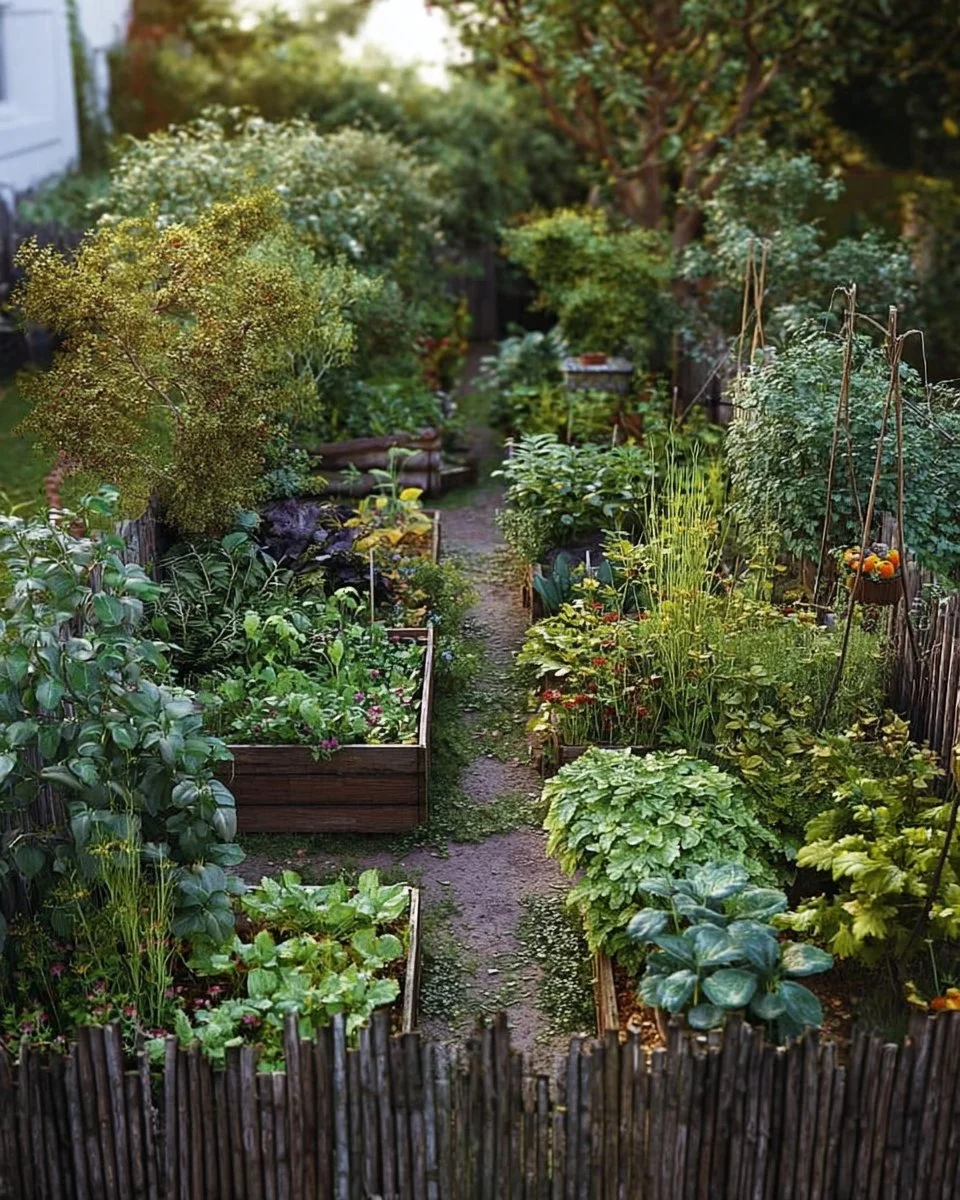
Introduction to Growing an Edible Garden: What to Plant
Have you ever thought about the joys of cultivating your own food? Growing an edible garden can be a rewarding experience that not only brings fresh produce to your table but also adds beauty to your outdoor space. Imagine stepping outside to pick ripe tomatoes, fragrant herbs, or crunchy cucumbers. It’s a wonderful way to connect with nature and understand where your food comes from.
In today’s fast-paced world, the simplicity of planting your own edible garden appeals to many. Whether you have a large backyard or just a small balcony, there’s a way for everyone to get involved. The best part? It’s practical and can be done on a budget. With time, effort, and a bit of planning, you can create your little slice of edible paradise.
What’s so special about growing an edible garden? It’s not just about saving money on groceries; it’s also about engaging in a healthy lifestyle. You’ll learn to appreciate the taste of fresh goods, while your family enjoys healthier meal options. Plus, nurturing plants can be a therapeutic hobby that fits right into your daily routine, whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned gardener.
With the right knowledge, anyone can start their own edible garden. It’s an affordable project, with many seeds and plants available at low prices. Depending on your skills, you can create a simple layout or a more complex design. Plus, time requirements are flexible—some plants thrive with little maintenance, making them ideal for busy schedules.
Table of Contents
Key Benefits of Growing an Edible Garden: What to Plant
Why You’ll Love This Build
- Freshness: Enjoy produce that’s freshly picked and bursting with flavor.
- Cost-Effective: Save money on groceries by growing your own food.
- Customizable: Choose plants that suit your tastes and dietary needs.
- Therapeutic: Gardening is known to reduce stress and boost mental health.
- Environmental Impact: Grow without the chemicals found in commercial produce.
- Educational: Learn about gardening, plant biology, and seasonal cycles.
What Makes It Stand Out
Growing an edible garden stands out because it offers a rewarding balance between work and relaxation. You can immerse yourself in the natural world while creating something beautiful and functional. The level of customization is another significant factor—whether you prefer vegetables, herbs, or fruits, you have endless choices.
Compared to store-bought produce, home-grown options are fresher and devoid of preservatives. The taste is unparalleled; many people find that home-grown vegetables far surpass what they find at the market. By focusing on sustainability, you’re also reducing your carbon footprint, making your edible garden a venture with a positive environmental impact.
Project Specs for Growing an Edible Garden: What to Plant
At-a-Glance Details
- Skill Level: Beginner to Intermediate
- Estimated Time: Ongoing (initial setup around 1-2 weekends)
- Estimated Cost (USD): $50-$200 (depending on scale and choice of plants)
- Dimensions: Varies based on available space (can be as small as a few pots)
- Indoor/Outdoor Suitability: Primarily outdoor with options for indoor herbs
- Tools Needed at a Minimum: Trowel, watering can, compost bin
Materials and Tools for Growing an Edible Garden: What to Plant
Complete Materials List with Measurements
- Seeds/Seedlings: Select according to preference (e.g., tomatoes, peppers, herbs)
- Soil: 2-3 bags of potting mix or garden soil (1.5 cu ft each)
- Compost: 1-2 bags (for enriching soil)
- Mulch: 1-2 bags (for moisture retention)
- Planters/Pots: Size varies (standard: 12-inch pots)
- Garden Bed Materials: If building beds: lumber (e.g., cedar boards: 4”x4”x8’)
- Fencing (if needed): 4-foot height for pest control
Complete Tools List
- Trowel: For planting and digging
- Watering Can: For easy watering
- Garden fork: For soil aeration
- Gloves: To protect hands
- Kneeling pad: For comfort during planting
Substitutes and Alternatives
If you’re on a tight budget or your favorite materials are unavailable, consider using repurposed containers for planting, such as old buckets or recycled bottles. As for soil, you can make your own compost by collecting kitchen scraps and yard waste. It’s a fantastic way to enrich your garden naturally.
If certain seeds or seedlings aren’t available in your area, you can often find them online or at local garden exchanges. This community aspect not only helps you find rare plants but also connects you with fellow gardeners.
Cut List and Measurements for Growing an Edible Garden: What to Plant
- Lumber for Raised Beds:
- 4 boards at 8’ (2.4 m) long for sides
- 4 boards at 4’ (1.2 m) long for ends
- Space for Planting:
- Allow 12” (30 cm) between plants
- Allow 24” (60 cm) for walking paths
No specific pilot holes for planting; ensure proper spacing for roots.
Safety and Prep for Growing an Edible Garden: What to Plant
When preparing for your edible garden, wearing Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) like garden gloves helps prevent cuts and scrapes. Ensure your workspace is clear of debris. Measure and mark your planting areas carefully, as accuracy is vital for maximizing space and plant health.
It’s also important to use labels for your seedlings to keep track of what you’ve planted. This helps avoid confusion and ensures proper care for each type of plant. When working outside, ensure adequate ventilation to avoid any harsh fumes from chemicals or fertilizers.
How to Build Growing an Edible Garden: What to Plant – Step-by-Step Directions
Step 1 – Prep and Layout
Begin by selecting the best spot for your edible garden. The location should ideally receive at least 6-8 hours of sunlight daily. Mark your planting area using stakes and string to visualize space usage.
Step 2 – Cut and Label Pieces
If you are building raised beds, cut your lumber according to the measurements outlined previously. Label each piece using waterproof markers to ensure clarity during assembly.
Step 3 – Dry Fit and Mark Joinery
Before final assembly, dry fit all components to ensure they fit correctly. Use clamps to hold boards together temporarily. Mark where you’ll drill pilot holes for easier assembly later.
Step 4 – Assemble the Frame/Body
Assemble your raised bed frame by screwing together the corners. Use exterior-grade screws for durability. Ensure the frame is square by measuring diagonally from one corner to the opposite.
Step 5 – Reinforce and Square
After mounting the frame, check for squareness again to prevent any issues with racking. Use scrap wood or braces to reinforce corners, ensuring they stay strong as the soil weight increases.
Step 6 – Attach Surfaces or Panels
If your design includes a bottom (common in container gardening), secure it using screws and ensure gaps are minimal to retain soil and moisture while allowing drainage.
Step 7 – Sanding and Edge Treatment
Smooth out any rough edges using sandpaper or a power sander. This prevents splinters and makes the structure more appealing. Clean off all dust thoroughly before moving on to planting.
Step 8 – Finish Application
If desired, apply an organic finish like a natural wood sealant to protect your raised beds from moisture. Wait for drying time as indicated by product instructions before planting.
Step 9 – Plant Your Seeds or Seedlings
Follow your planting guide based on the type of vegetables or herbs you have chosen. Make small indentations in the soil according to seed depth requirements and evenly space them based on plant size.
Step 10 – Water and Maintain
After planting, water the area thoroughly. Incorporate a schedule for watering and maintenance, adjusting for seasonal changes. Regularly check for pests and diseases to keep your garden healthy.
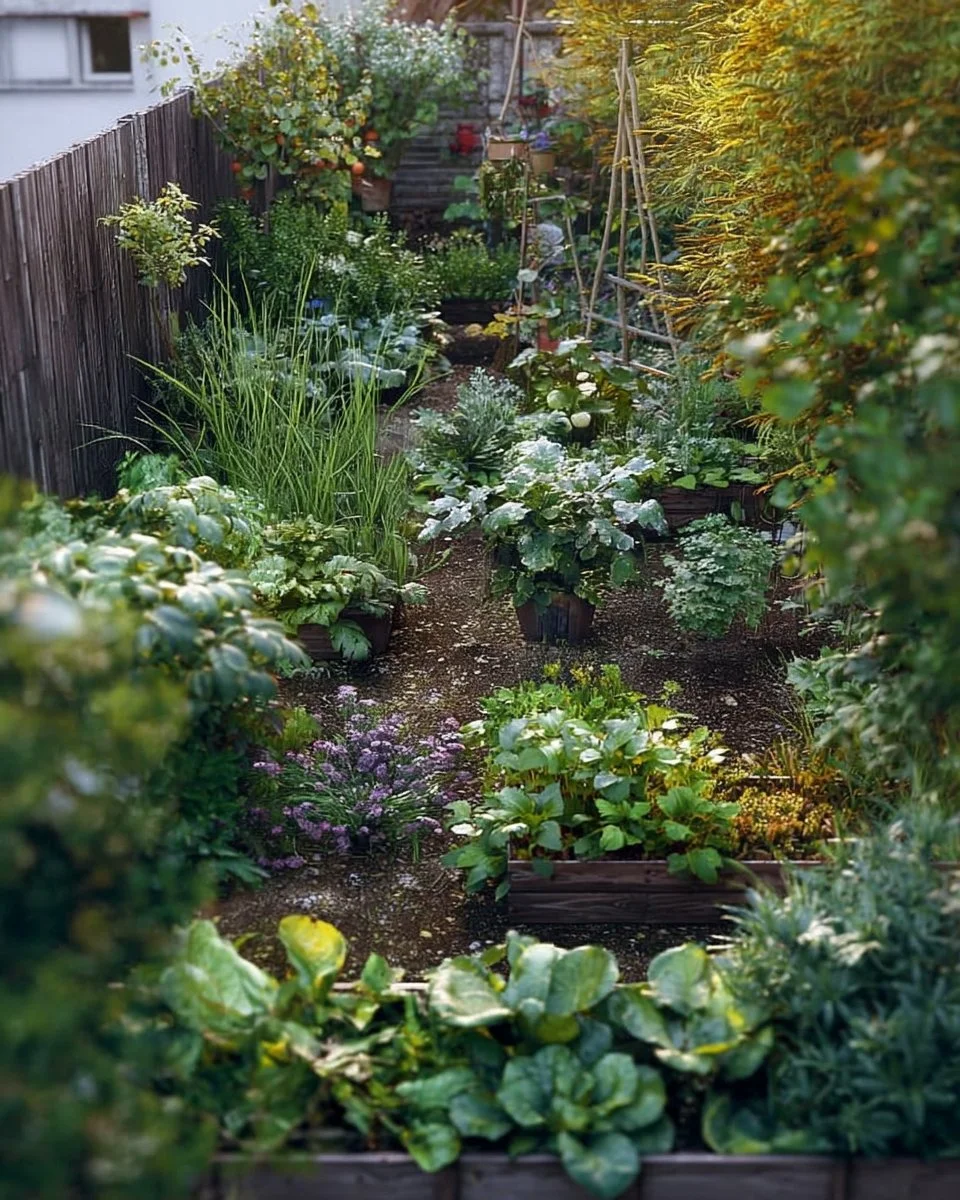

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the best plants for beginners?
Start with easy-to-grow options like tomatoes, lettuce, and herbs.
How often should I water my garden?
Generally, watering 2-3 times a week is ideal, depending on your climate.
What kind of soil is best for an edible garden?
Loamy soil enriched with compost works best for most vegetables.
How do I protect my garden from pests?
Consider using natural repellents, companion planting, or physical barriers like row covers.
Can I grow an edible garden in pots?
Absolutely! Just ensure your pots provide adequate drainage and space for roots.
What is the best time to plant?
It depends on your location, but most vegetables do well in the spring and fall seasons.
With a bit of planning and care, you’ll be well on your way to enjoying the delights of your own edible garden. Happy gardening!